What is letter spacing in CSS?
In CSS, letter spacing is a property that allows you to control the amount of space between individual characters in text. It can be used to increase or decrease the space between letters for a desired visual effect.
What is the main purpose of letter spacing in CSS?
The main purpose of letter spacing in CSS is to control the spacing between individual characters in text for visual enhancement and design purposes. It can be used to adjust the readability, aesthetics, and overall appearance of the text on a webpage.
How to use letter spacing in CSS?
To use letter spacing in CSS, you can use the "letter-spacing" property. For example, if you want to increase the spacing between letters, you can set it to a positive value like "2px". If you want to decrease the spacing, you can set it to a negative value like "-1px". Here's an example:
p {
letter-spacing: 2px;
}
This will apply a letter spacing of 2 pixels to all paragraphs on your webpage.
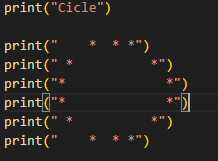
Example:
Then the output will be:
What is Border-width in CSS?
In CSS, "border-width" is a property that allows you to control the thickness of the border around an element. It can be specified in different units such as pixels, em, or percentages. For example, you can set the border width to "2px" to create a thin border or "10px" to create a thicker border.
What is the main purpose of Border-width in CSS?
The main purpose of border width in CSS is to define the thickness or width of the border around an element. It helps control the visual appearance and style of the border, allowing you to create different effects and emphasize elements on a webpage.
How to use the Border-width in CSS?
To use border width in CSS, you can specify the desired width using the "border-width" property. For example, if you want to set the border width to 2 pixels, you can use the following CSS code:
.element {
border-width: 2px;
}
This will apply a border with a width of 2 pixels to the selected element. You can also use other units like em, rem, or percentages to define the border width.
Example:
Then the output will be: